Difference between revisions of "SHA-3 Hardware Implementations"
m (→High-Speed Implementations (ASIC): Updated technology entries for Luffa implementation of Knežević and Verbauwhede) |
m (→Low-Area Implementations (ASIC): Added low-area implementations of Luffa from Knežević and Verbauwhede) |
||
| Line 289: | Line 289: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Luffa-224/256 || [http://www.sdl.hitachi.co.jp/crypto/luffa/Luffa_SupportingDocument.pdf Supporting document] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || One permutation block (One S-box, one MixWord block) || 0.13 µm || align="right"| 10.16 kGates || align="right"| 28.7 Mbit/s || align="right"| 100 MHz | | Luffa-224/256 || [http://www.sdl.hitachi.co.jp/crypto/luffa/Luffa_SupportingDocument.pdf Supporting document] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || One permutation block (One S-box, one MixWord block) || 0.13 µm || align="right"| 10.16 kGates || align="right"| 28.7 Mbit/s || align="right"| 100 MHz | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Luffa-224/256 || [http://www.cosic.esat.kuleuven.be/publications/article-1282.pdf Knežević and Verbauwhede] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) || UMC 0.13 µm || align="right"| 18.26 kGates || align="right"| 2461 Mbit/s || align="right"| 250 MHz | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Luffa-384 || [http://www.cosic.esat.kuleuven.be/publications/article-1282.pdf Knežević and Verbauwhede] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) || UMC 0.13 µm || align="right"| 27.13 kGates || align="right"| 1882 Mbit/s || align="right"| 250 MHz | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Luffa-512 || [http://www.cosic.esat.kuleuven.be/publications/article-1282.pdf Knežević and Verbauwhede] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) || UMC 0.13 µm || align="right"| 37.35 kGates || align="right"| 1524 Mbit/s || align="right"| 250 MHz | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Skein-256-256 || [http://eprint.iacr.org/2009/349.pdf Tillich et al.] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || 64-bit datapath || AMS 0.35 µm || align="right"| 12.89 kGates || align="right"| 19.8 Mbit/s || align="right"| 80 MHz | | Skein-256-256 || [http://eprint.iacr.org/2009/349.pdf Tillich et al.] || [[#Fully_Autonomous_Implementation|Fully autonomous]] || 64-bit datapath || AMS 0.35 µm || align="right"| 12.89 kGates || align="right"| 19.8 Mbit/s || align="right"| 80 MHz | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 4 November 2009
Contents
1 Important Information
This page summarizes key properties of reported hardware implementations of those SHA-3 candidates, which are currently under consideration by NIST. This is work in progress.
A list of hardware implementations of the round 1 candidates can be found here. Please note that the page for round 1 candidates is provided for reference and will not be updated.
The implementations are categorized into FPGA and standard-cell ASIC implementations. Note that the diversity of implementation scope, target technologies, and synthesis tools makes direct comparisions between different hardware implementation difficult. The more of these parameters agree, the more reasonable the comparison becomes.
The target technology should be as similar as possible. For FPGA implementation, it is desirable to compare implementations on the same target device (or at least on devices of the same FPGA family). For standard-cell ASIC implementation, at least the minimal gate length of the process (e.g., 0.13 µm) should agree. More ideally, the implementations use the same standard-cell library (which implies the use of the same process technology).
In order to facilitate the comparision of hardware modules with different implementation scopes, we classify them into three categories:
For suggestions regarding the structure of this site, let us know at sha3zoo-hardware@iaik.tugraz.at
1.1 Fully Autonomous Implementation
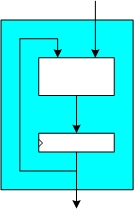
Such hardware implementations include the complete functionality of a SHA-3 candidate (or a specific version thereof). That means the input message can be loaded piecewise into the hardware module and it delivers the message digest as output. All hash calculations happen exclusively within the hardware module. If integrated in a system, the achievable throughput of a fully autonomous implementation depends on the speed of the hardware module itself and the speed of the (system dependent) data interface delivering the input message.
1.2 Implementation with External Memory
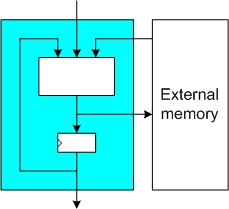
These implementations use external memory to hold intermediate values during the hashing of a message. The implemented hardware itself normally consists of the core logic functionality of the hash function, some registers for short-lived temporary values, and possible a memory controller for access to the external memory. Such implementations can load the input message either over a dedicated interface (similar to a fully autonomous implementation) or from the external memory. In order to reach the maximal throughput of the hardware module, the external memory must be sufficiently fast.
1.3 Implementation of Core Functionality
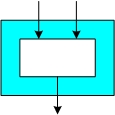
Such implementations comprise only important parts of the hash function (e.g., the compression function), which normally allows to get a first-order estimate of the performance figures of full implementations.
2 High-Speed Implementations (FPGA)
Important note: The size and functionality of slices varies between FPGA families. A direct comparision of the slice count of implementations on different FPGA families is therefore problematic.
| Hash Function Name | Reference | Impl. Scope | Impl. Details | Technology | Size | Throughput | Clock Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex-II Pro | 3091 slices | 1724 Mbit/s | 37.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex 4 | 3087 slices | 2235 Mbit/s | 48.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1694 slices | 3103 Mbit/s | 67.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units and I/O registers | Altera Stratix III | 5435 ALUTs | 2186.2 Mbit/s | 46.97 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex-II Pro | 11122 slices | 1177 Mbit/s | 17.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex 4 | 11483 slices | 1707 Mbit/s | 25.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 4329 slices | 2389 Mbit/s | 35.0 MHz |
| Blue Midnight Wish-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with f0, f1, and f2 unrolled in sequence and I/O registers | Altera Stratix III | 12917 ALUTs | 4889.6 Mbit/s | 9.55 MHz |
| CubeHash8/1-256 | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 2 compression functions unrolled | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 3268 slices | 70 Mbit/s | 37.9 MHz |
| CubeHash8/1-256 | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 1 iterated compression function | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1178 slices | 160 Mbit/s | 166.8 MHz |
| ECHO-224/256 | Lu et al. | Fully autonomous | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 9333 slices | 14860 Mbit/s | 87.1 MHz | |
| ECHO-384/512 | Lu et al. | Fully autonomous | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 9097 slices | 7810 Mbit/s | 83.9 MHz | |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Jungk et al. | Fully autonomous | P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 6136 slices | 4520 Mbit/s | 88.3 MHz |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1722 slices | 10276 Mbit/s | 200.7 MHz |
| Grøstl-384/512 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 20233 slices | 5901 Mbit/s | 80.7 MHz |
| Grøstl-384/512 | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | P & Q permutation interleaved, S-box in BRAM | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 6313 slices | 2910 Mbit/s | 79.61 MHz |
| Grøstl-384/512 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 5419 slices | 15395 Mbit/s | 210.5 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) & IO buffer | Altera Cyclone III | 5776 LEs | 7500 Mbit/s | 133 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) & IO buffer | Altera Stratix III | 4713 ALUTs | 12400 Mbit/s | 218 MHz |
| Keccak | Joachim Strömbergson | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) only | Xilinx Spartan 3A | 3393 slices | 4800 Mbit/s | 85 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) & IO buffer | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1412 slices | 6900 Mbit/s | 122 MHz |
| Luffa-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function (1 cycle latency) and I/O registers | Altera Stratix III | 16552 ALUTs | 12042.2 Mbit/s | 47.04 MHz |
| Shabal | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 36 adders in permutation | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 2223 slices | 740 Mbit/s | 71.48 MHz |
| Shabal | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 36 adders in permutation | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 2768 slices | 1450 Mbit/s | 138.87 MHz |
| Shabal-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with I/O registers (latency of 16 clock cycles) | Altera Stratix III | 1440 ALUTs | 3125.6 Mbit/s | 195.35 MHz |
| Skein-256 | Men Long | Core functionality | UBI component | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1001 slices | 408.7 Mbit/s | 114.9 MHz |
| Skein-256 | Stefan Tillich | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 937 slices | 1751 Mbit/s | 68.4 MHz |
| Skein-256 | Stefan Tillich | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 2421 slices | 669 Mbit/s | 26.14 MHz |
| Skein-512 | Men Long | Core functionality | UBI component | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1877 slices | 817.4 Mbit/s | 114.9 MHz |
| Skein-512 | Stefan Tillich | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 1632 slices | 3535 Mbit/s | 69.04 MHz |
| Skein-512 | Stefan Tillich | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 4273 slices | 1365 Mbit/s | 26.66 MHz |
3 Low-Area Implementations (FPGA)
| Hash Function Name | Reference | Impl. Scope | Implementation Details | Technology | Size | Throughput | Clock Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex-II Pro | 958 slices | 371 Mbit/s | 59.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex 4 | 960 slices | 430 Mbit/s | 68.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 390 slices | 575 Mbit/s | 91.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex-II Pro | 1802 slices | 326 Mbit/s | 36.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex 4 | 1856 slices | 381 Mbit/s | 42.0 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 1 G function unit | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 939 slices | 533 Mbit/s | 59.0 MHz |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Jungk et al. | Fully autonomous | 64-bit datapath, P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 2486 slices | 404 Mbit/s | 63.2 MHz |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Jungk et al. | Fully autonomous | 64-bit datapath, P & Q permutation in parallel | Xilinx Virtex 2 Pro | 2754 slices | 512 Mbit/s | 81.5 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Using external memory | Small core using system memory | Altera Stratix III | 855 ALUTs | 96.8 Mbit/s | 366 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Using external memory | Small core using system memory | Altera Cyclone III | 1559 LEs | 47.8 Mbit/s | 181 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Using external memory | Small core using system memory | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 444 slices | 70.1 Mbit/s | 265 MHz |
| Shabal | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 1 adder in permutation | Xilinx Spartan 3 | 1933 slices | 540 Mbit/s | 89.71 MHz |
| Shabal | Baldwin et al. | Core functionality | 1 adder in permutation | Xilinx Virtex 5 | 2307 slices | 1330 Mbit/s | 222.22 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | One round of Threefish iterated | Altera Stratix III | 1385 ALUTs | 573.9 Mbit/s | 161.42 MHz |
4 High-Speed Implementations (ASIC)
A comparison of implementations of all 14 round 2 candidates has been presented informally at IAIK (Graz University of Technology) on Sept. 16, 2009. The presentation slides can be found here.
The rows shaded in gray are results of a benchmarking of implementations of all 14 candidates on the same technology. For a graphical comparison of these results, refer to the original publication here.
| Hash Function Name | Reference | Impl. Scope | Implementation Details | Technology | Size | Throughput | Clock Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.30 kGates | 5295 Mbit/s | 114 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 4 G function units | UMC 0.18 µm | 41.31 kGates | 4153 Mbit/s | 170 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units and I/O registers | STM 90 nm | 53 kGates | 4475 Mbit/s(*) | 96.15 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Compression function with 4 G function units with CSAs | UMC 0.18 µm | 45.64 kGates | 3971 Mbit/s | 170.64 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 8 G function units | UMC 0.18 µm | 132.47 kGates | 5910 Mbit/s | 87 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with 4 G function units | UMC 0.18 µm | 82.73 kGates | 4810 Mbit/s | 136 MHz |
| Blue Midnight Wish-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with f0, f1, and f2 unrolled in sequence and I/O registers | STM 90 nm | 164 kGates | 26665 Mbit/s(*) | 52.08 MHz |
| Blue Midnight Wish-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 40 32-bit adders shared by f0, f1, and f2, two temporary 512-bit states | UMC 0.18 µm | 122.09 kGates | 1586 Mbit/s | 164.20 MHz |
| CubeHash16/32-h | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Dynamically reconfigurable r and b parameters, two rounds unrolled | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.87 kGates | 4665 Mbit/s | 145.77 MHz |
| ECHO-224/256 | Lu et al. | Fully autonomous | 0.13 µm | 521.1 kGates | 14850 Mbit/s | 87.1 MHz | |
| ECHO-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Four parallel AES rounds, 16 AES MixColumns 32-bit column multipliers | UMC 0.18 µm | 141.49 kGates | 2246 Mbit/s | 141.84 MHz |
| ECHO-384/512 | Lu et al. | Fully autonomous | 0.13 µm | 516.8 kGates | 7750 Mbit/s | 83.3 MHz | |
| Fugue-256 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | Four columns of SMIX transformation in parallel (SUPER4_P) | IBM 90 nm | 109.85 kGates | 13913 Mbit/s | 869.5 MHz |
| Fugue-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Four columns of SMIX transformation in parallel | UMC 0.18 µm | 46.26 kGates | 4092 Mbit/s | 255.75 MHz |
| Grøstl-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | One shared permutation for P & Q, one pipeline stage | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.40 kGates | 6290 Mbit/s | 270.27 MHz |
| Grøstl-384/512 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | P & Q permutation in parallel | UMC 0.18 µm | 341 kGates | 6225 Mbit/s | 85.1 MHz |
| Hamsi-256 | Junfeng Fan (Hamsi website) | Fully autonomous | 0.13 µm | 22 kGates | 4940 Mbit/s | 1080 MHz | |
| Hamsi-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Three instances of P/Pf function unrolled | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.66 kGates | 5565 Mbit/s | 173.91 MHz |
| Hamsi-512 | Junfeng Fan (Hamsi website) | Fully autonomous | 0.13 µm | 50 kGates | 3970 Mbit/s | 820 MHz | |
| JH-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 320 S-boxes, one round of R8 per cycle | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.83 kGates | 4991 Mbit/s | 380.22 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) & IO buffer | ST 0.13 µm | 48 kGates | 29900 Mbit/s | 526 MHz |
| Keccak | Submission document | Fully autonomous | Core (round function, state register) only | ST 0.13 µm | 40 kGates | 15000 Mbit/s | 500 MHz |
| Keccak(-256) | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | One instance of Keccak-f round | UMC 0.18 µm | 56.32 kGates | 21229 Mbit/s | 487.80 MHz |
| Luffa-224/256 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | Three permutation blocks in parallel (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks each) | UMC 0.13 µm | 30.83 kGates | 31960 Mbit/s | 1124 MHz |
| Luffa-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function (1 cycle latency) and I/O registers | STM 90 nm | 122 kGates | 25702 Mbit/s(*) | 100.4 MHz |
| Luffa-224/256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Three permutation blocks in parallel (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks each) | UMC 0.18 µm | 44.97 kGates | 13741 Mbit/s | 483.09 MHz |
| Luffa-384 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | Four permutation blocks in parallel (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks each) | UMC 0.13 µm | 50.07 kGates | 23126 Mbit/s | 813 MHz |
| Luffa-512 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | Five permutation blocks in parallel (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks each) | UMC 0.13 µm | 65.1 kGates | 19617 Mbit/s | 690 MHz |
| Shabal-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | Compression function with I/O registers (latency of 16 clock cycles) | STM 90 nm | 20 kGates | 4408 Mbit/s(*) | 413.22 MHz |
| Shabal-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | One word rotation per cycle, 50 cycles per block | UMC 0.18 µm | 54.19 kGates | 3282 Mbit/s | 320.51 MHz |
| SHAvite-3256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Four AES rounds (two for compression, two for message expansion) | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.83 kGates | 2387 Mbit/s | 88.57 MHz |
| SIMD-256(**) | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | Two FFT-64 with two FFT-8 and 16 multipliers (8x8 bit) each | UMC 0.18 µm | 104.17 kGates | 924 Mbit/s | 64.93 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Stefan Tillich | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | UMC 0.18 µm | 53.87 kGates | 1762 Mbit/s | 68.8 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | All 72 Threefish rounds unrolled | STM 90 nm | 369 kGates | 3126 Mbit/s(*) | 12.21 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | UMC 0.18 µm | 58.61 kGates | 1882 Mbit/s | 73.52 MHz |
| Skein-512-512 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 8 Threefish rounds unrolled | UMC 0.18 µm | 102.04 kGates | 2502 Mbit/s | 48.87 MHz |
(*) Estimated peak throughput for the minimal delay of compression function: 1000 * (Input Size in bits) / [(Compression Function Delay in ns) * (Number of Cycles)] = Throughput in Mbit/s (**) Implementation of round-one variant.
5 Low-Area Implementations (ASIC)
| Hash Function Name | Reference | Impl. Scope | Implementation Details | Technology | Size | Throughput | Clock Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLAKE-32 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | One G function in 11 cycles | AMS 0.35 µm | 25.57 kGates | 15.4 Mbit/s | 31.25 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with a single G function unit | UMC 0.18 µm | 10.54 kGates | 253 Mbit/s | 40 MHz |
| BLAKE-32 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with a half G function unit | UMC 0.18 µm | 9.89 kGates | 127 Mbit/s | 40 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with a single G function unit | UMC 0.18 µm | 20.61 kGates | 181 Mbit/s | 20 MHz |
| BLAKE-64 | Submission document | Core functionality | Compression function with a half G function unit | UMC 0.18 µm | 19.46 kGates | 91 Mbit/s | 20 MHz |
| ECHO-224/256 | Lu et al. | Fully autonomous | 0.13 µm | 82.8 kGates | 373 Mbit/s | 66.6 MHz | |
| Fugue-256 | Submission document | Fully autonomous | One SMIX transformation (SUPER1_L) | IBM 90 nm | 59.22 kGates | 2000 Mbit/s | 500 MHz |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 64-bit datapath, P & Q permutation shared | AMS 0.35 µm | 14.62 kGates | 145.9 Mbit/s | 55.87 MHz |
| Grøstl-224/256 | Grøstl website | Fully autonomous | 64-bit datapath, P & Q permutation shared | UMC 0.18 µm | 17 kGates | 645 Mbit/s | 246.9 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Using external memory | Small core using system memory | ST 0.13 µm | 6.5 kGates | 176.4 Mbit/s(*) | 666.7 MHz |
| Keccak | Updated specification (v1.2) | Using external memory | Small core using system memory, clock freq. limited to 200 MHz | ST 0.13 µm | 5 kGates | 52.9 Mbit/s(**) | 200 MHz |
| Luffa-224/256 | Supporting document | Fully autonomous | One permutation block (One S-box, one MixWord block) | 0.13 µm | 10.16 kGates | 28.7 Mbit/s | 100 MHz |
| Luffa-224/256 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) | UMC 0.13 µm | 18.26 kGates | 2461 Mbit/s | 250 MHz |
| Luffa-384 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) | UMC 0.13 µm | 27.13 kGates | 1882 Mbit/s | 250 MHz |
| Luffa-512 | Knežević and Verbauwhede | Fully autonomous | One permutation block (64 S-boxes, 4 MixWord blocks) | UMC 0.13 µm | 37.35 kGates | 1524 Mbit/s | 250 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Tillich et al. | Fully autonomous | 64-bit datapath | AMS 0.35 µm | 12.89 kGates | 19.8 Mbit/s | 80 MHz |
| Skein-256-256 | Namin and Hasan | Core functionality | One round of Threefish iterated | STM 90 nm | 21 kGates | 1018.8 Mbit/s(***) | 286.53 MHz |
(*) Estimation for 64-bit memory interface: (1024 bits/permutation) * (666.7 * 10^6 cycles/s) / (3870 cycles/permutation) = 176.41 * 10^6 bits/s
(**) Estimation for 64-bit memory interface: (1024 bits/permutation) * (200 * 10^6 cycles/s) / (3870 cycles/permutation) = 52.92 * 10^6 bits/s
(***) Estimated peak throughput for the minimal delay of compression function: 1000 * (Input Size in bits) / [(Compression Function Delay in ns) * (Number of Cycles)] = Throughput in Mbit/s
6 Call for contributions
Implementers (both submitters and non-submitters): You have results that complement this site? Let us know at sha3zoo-hardware@iaik.tugraz.at